What Is a BLS Certification? Overview and FAQ
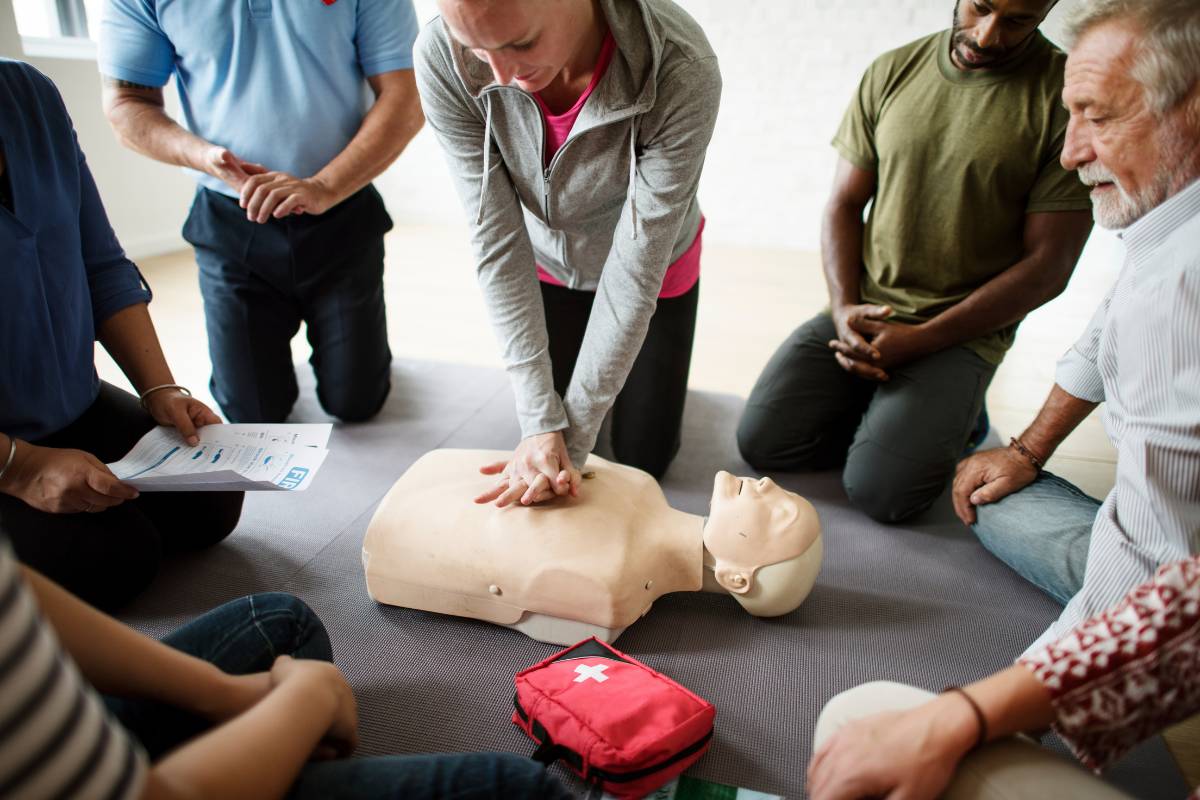
Nurses have many specialties and credentials they can choose to pursue, but there are certain areas of training that are nearly universal. One example is becoming certified in basic life support (BLS) protocol. In this article, we’ll explain what BLS certification is, why BLS cert credentials are important, how to become BLS certified, and more.
What Is BLS Certification?
Basic life support certification is proof that you have obtained approved training so that you know what to do if a patient stops breathing, loses a pulse, or has an obstruction in their airway. Nearly every patient-facing role in acute care and post-acute settings requires BLS training, and you may need to get certified before you begin nursing school.
The American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Red Cross are the main providers of BLS courses, and facilities tend to prefer one over the other. Although the content of each BLS course won’t differ — much of BLS training involves physical skills, such as giving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and ventilation — if this is your first time becoming BLS certified, check with your institution or employer to understand which training organization they’ll accept.
Healthcare settings that typically require BLS certification include:
- Ambulatory care
- Correctional facilities
- Emergency departments
- Inpatient units
- Operating rooms
- Psychiatric hospitals
- Surgical centers
- Urgent care clinics
What Is a BLS Certificate Supposed to Teach?
Earning a BLS certificate issued by the AHA shows that you’ve had training in these procedures:
- Giving high-quality CPR to infants, children, and adults
- Implementing the AHA Chain of Survival
- Operating an automatic external defibrillator (AED)
- Giving ventilations using an oral barrier device or ambu-bag
- Using teamwork in multi-rescue CPR
- Responding to foreign-body airway obstruction (choking) in adults and children
Research shows that after nurses received formal life-support training, patient survival from cardiac arrests jumped from 28% to 53%.
The Five Steps of BLS
What is a BLS certification training course going to cover? The five steps of BLS are a structured workflow for assessing the patient and situation and giving life-saving interventions. You’ll learn more about the five steps in a BLS class, but here’s a brief overview:
- Ensure the scene is safe.
- Check responsiveness, and if the patient does not respond, call for help.
- Assess breathing and pulse.
- In the case of abnormal or absent breathing, give rescue breaths.
- In the case of absent breathing and pulse, begin giving CPR.
American Heart Association BLS Format Options
AHA offers two ways to go through this training — in-person instruction in a classroom or blended learning. The two formats teach the same skills, including single-rescuer CPR and team CPR, and you’ll receive the same BLS certificate no matter which format you choose. Keep in mind that BLS certification expires every two years, and to renew, you’ll need to do a review and a skills check-off to show you’re still proficient.
Here’s a breakdown of these two structures:
| Feature | In-Person BLS Training | Blended BLS Training |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Hands-on training provided by an instructor at an AHA training site | Combination of an online course and an in-person session at an AHA training site |
| Cost |
|
|
| Time | Initial training: 4.5 hours
Renewal: 3 hours |
Online portion: ~2 hours
Hands-on portion: 1–2 hour |
| CE/CME credit? | Yes. Log in to AHA’s CEU claiming site within 30 days of your class. | Yes. You’ll use your course login to claim your credits. |
Red Cross BLS Format Options
If your facility requires Red Cross BLS training, you’ll also have two options to complete this certification, which is valid for two years:
| Feature | In-Person BLS Training | Blended BLS Training |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Hands-on training provided by an instructor at an ARC training site | Online simulation, followed with in-person skills training |
| Cost |
|
|
| Time | Initial training: 4.5 hours
Renewals: 2.5 hours (must be in person) |
Online portion: 2 hours
Hands-on portion: 2.5 hours |
| CE/CME credit? | Only available for EMTs | Only available for EMTs |
BLS Certification: Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to get a BLS certification?
Most classes take just half a day. The AHA’s BLS provider course takes four and a half hours, and renewals take three hours. Typically, courses include a didactic component, a physical skills practice, then a written exam and a skills check-off.
What is the BLS certification exam like?
These exams include 25 test questions and are generally open-book. You’ll get an hour to complete the exam and need to earn a minimum grade of 84% to pass.
Does a BLS certification cover child and infant CPR?
Yes, a BLS course covers protocols for infants and children. If you’re a nurse looking for more specialized courses for emergency pediatric care, check out a pediatric advanced life support (PALS) course. This includes basic life support interventions, as well as advanced medications and interventions for saving pediatric lives.
What is a BLS certification compared to CPR?
BLS is distinct from CPR training in two main ways:
1. Depth of Information
BLS is a more comprehensive course than CPR, and contains CPR training with additional skills. It’s designed for people who are more likely to encounter cardiovascular emergencies in their work, and includes systems for providing resuscitation as an individual and a team member.
AHA’s BLS also incorporates the Chain of Survival, which is designed to give patients the best outcomes after cardiovascular emergencies. CPR, on the other hand, covers essential topics like chest compressions, operating an AED, and giving rescue breaths.
These skills might also be accompanied with basic first-aid training. BLS deepens these skills, adding advanced airway management and specialized techniques for the healthcare setting. Even though BLS builds on these skills, you don’t need to be CPR trained to sign up for a BLS course.
2. Job Requirement
BLS is a requirement in nearly every role in healthcare, whether you’re a medication aide or a chief nursing officer. CPR courses are taught to laypeople who want to learn basic skills, while BLS is typically taught to medical personnel (although anyone can pursue it).
Professionals who are typically CPR certified include:
- Lifeguards
- Babysitters and nannies
- Teachers and school staff
- Coaches and fitness instructors
- Security personnel
- Restaurant staff
Professionals who are typically BLS certified include:
- Nurses
- Certified nurse assistant (CNAs)
- Physicians and medical residents
- Respiratory therapists
- Police
- Firefighters
- First responders
What is a BLS certification compared to ACLS?
ACLS stands for advanced cardiac life support. Both certifications are for healthcare professionals, but ACLS contains more advanced skills, medications, and protocols. Nurses in intermediate settings will be BLS certified, while nurses in critical care receive ACLS as well.
If a patient codes on the floor, staff need to respond and treat them quickly with BLS protocols to transfer them to the ICU. When a patient codes in the ICU, they’re there to stay, so these nurses need more advanced life-saving skills covered by ACLS.
Where can you get a BLS certification?
The leading organizations offering BLS training today are the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Red Cross. Your facility will likely have a preference between the two — for example, AHA BLS is preferred by many schools and hospitals. In most areas, you’ll likely be able to find a BLS class at a local community college, hospital, or other teaching facility. Some organizations offer free BLS certification or BLS certification online, but be sure that your facility will accept your certification before you enroll in these options.
Related Certifications
- Cardiopulmonary Rescue (CPR)
- American Medical Technologists Certification (AMT)
- Pediatric Emergency Assessment, Recognition, Stabilization (PEARS)
- National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
- Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP)
- S.T.A.B.L.E. Certification
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
Find Your Next Nursing Role
What is a BLS certification going to help you achieve? With IntelyCare, you can get access to nursing roles tailored to your specifications. Find out how you can receive personalized nursing jobs, right to your inbox.

