21 Basic Nursing Skills You’re Taught in School
Think of basic nursing skills as the foundation of your professional instincts. From taking vital signs and assisting with mobility to administering medications and performing wound care, these skills prepare you to switch seamlessly between tasks in the unpredictable world of patient care, where emergencies and routine care often happen side by side.
But what nursing skills are absolutely essential before entering the workplace? Below, we break down the key competencies you’ll master as a nursing student.
Basic Nursing Skills: The Essentials
Picture yourself in a busy emergency department. A patient suddenly needs CPR, followed immediately by blood product administration, and ventilator support. In moments like these, there’s no time to pause and review your classroom notes. You have to act quickly, confidently, and correctly — almost on instinct.
To build that level of readiness, nursing school combines classroom learning, simulation labs, and clinical rotations. Here’s a breakdown of the core competencies every nursing student is taught — and expected to master — before earning a registered nurse (RN) title.
1. Vital Signs Assessment
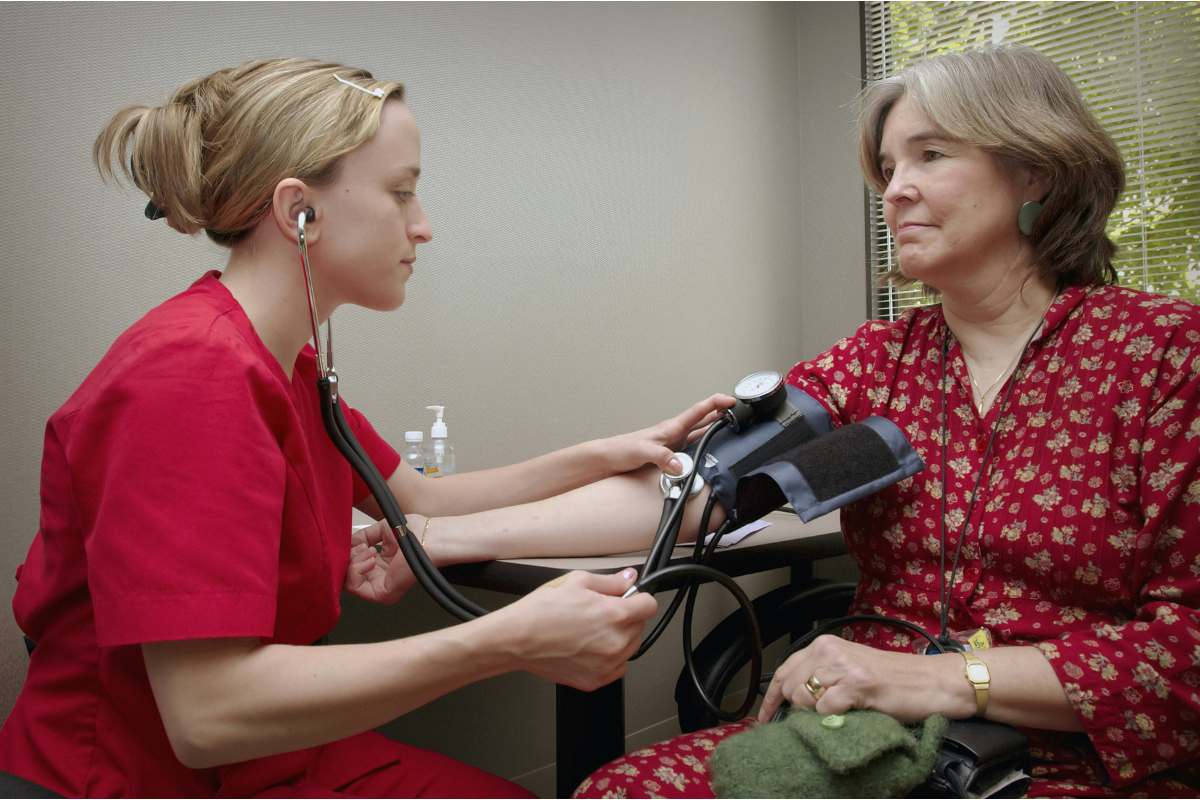
Taking vital signs is one of the first basic nursing skills taught in nursing school — but it’s far more than recording numbers. Nursing students learn to assess temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and pain in context. For example, a blood pressure of 90/60 may appear normal on paper, but if a patient’s baseline is typically 145/100 and that drop occurs within minutes, it can signal acute blood loss, sepsis, or shock.
Nursing education emphasizes trending vital signs over time, recognizing subtle changes, and knowing when to escalate concerns — skills that are critical for early intervention and patient safety.
2. Head-to-Toe Physical Assessment
A head-to-toe assessment is a systematic way for nurses to evaluate every part of a patient’s body, from neurological status and heart sounds to skin integrity and mental status. Nursing students are trained to inspect, palpate, auscultate, and percuss each body system to establish an individualized baseline, enabling the early detection of emerging clinical issues. For example, a little ankle swelling paired with mild shortness of breath could be an early sign of heart failure. Discovering this in an assessment lets the team step in before the condition worsens.
3. IV Therapy
Nursing students spend a lot of time practicing IV therapy because it’s critical in nearly every clinical setting. This includes inserting peripheral lines, maintaining patency, administering fluids, and monitoring infusion sites for complications such as infiltration, phlebitis, or infection. Students also learn the basics of administering certain high-risk medications — like potassium, chemotherapy agents, and vasoactive drugs — that can be dangerous if dosed incorrectly or delivered too quickly.
4. Wound Care
Wound care is a skill nurses use in a variety of clinical environments, including surgical floors, intensive care units, rehabilitation centers, and long-term care facilities. Nursing students learn how to check wounds carefully — looking at size, depth, drainage, color, smell, and any signs of infection. They practice cleaning wounds, picking the right dressings, using sterile techniques, and documenting care properly.
5. Blood Product Administration
Administering blood and blood products is a critical clinical skill nurses must master because it involves both lifesaving potential and serious risk. Nursing students learn that the process begins long before the first drop of blood enters the patient’s veins. This includes verifying the provider’s order, checking blood compatibility, and confirming informed consent. They also learn to spot early signs of complications, such as fever, chills, back pain, or shortness of breath, and respond immediately to keep patients safe.
6. Specimen Collection
You might think collecting specimens — like blood, urine, or swabs — is straightforward, but there’s a lot more to it than meets the eye. Nursing students learn the correct techniques for collecting, labeling, and handling specimens to ensure accurate lab results. They also practice preventing contamination, because even a tiny lapse in proper handling can result in inaccurate results, misdiagnoses, and delays in treatment.
7. Foley Catheter Insertion and Urinary Care
Nursing students are trained in sterile technique for inserting, maintaining, and removing urinary catheters. They learn how to monitor urine output, prevent catheter-associated infections, and ensure patient comfort and dignity through the process. Mastering this skill helps students manage patients with urinary retention, post-surgical needs, or neurological disorders or injuries.
8. Bed Baths and Occupied Bed Changes
Bed baths and occupied bed changes might sound simple, but they’re an important part of hands-on nursing care. Nursing students learn how to clean and reposition patients who can’t get out of bed, while protecting their comfort and privacy. These moments are also key assessment opportunities — nurses check skin integrity, notice early pressure injuries, and assess mobility, all while using proper body mechanics to keep both the patient and themselves safe.
9. Oxygen Therapy and Airway Support
In nursing, everything starts with the ABCs: airway, breathing, and circulation. Nursing students learn that when a patient is struggling to breathe, nothing else matters until oxygenation is addressed. They’re trained to safely administer oxygen using nasal cannulas, simple masks, and non-rebreathers, while closely monitoring oxygen saturation and respiratory rate.
Students also learn airway support skills like suctioning to clear secretions that can block the airway — especially in patients who are weak, unconscious, or unable to cough effectively.
10. Nutrition and Feeding Assistance
No, it’s not just spoon-feeding. Nursing students also learn how to manage alternative feeding methods, like percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes, nasogastric (NG) tubes, and jejunostomy tubes. This includes checking placement, administering formula and medications safely, flushing tubes to prevent blockages, and monitoring for complications like infection, aspiration, or tube displacement. Mastery of these basic nursing skills helps ensure patients who cannot eat orally still receive proper nutrition, hydration, and medication support.
11. Mobility and Fall Prevention
Helping patients move safely is more than just lifting or walking with them — it’s also about preventing injuries and maintaining independence. Nursing students learn safe transfer techniques, proper use of gait belts, wheelchairs, and walkers, and how to reposition bedridden patients safely. They’re also trained to identify fall risks, implement safety measures, and adapt care for patients with weakness, balance issues, or post-surgical limitations.
12. Medication Administration
Medications can save lives — or cause serious harm if given incorrectly. That’s why nursing students spend a lot of time learning how to administer drugs via multiple routes, including oral, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, topical, and inhaled. They are trained to follow the five rights of medication administration — right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, and right time — while monitoring for side effects or adverse reactions.
Additionally, accurate calculations, careful documentation, and educating patients are all part of making sure each dose helps rather than harms.
13. Creating Nursing Care Plans
Creating nursing care plans is where critical thinking meets practical care. Nursing students learn to take all the data they gather — vital signs, assessments, lab results, and patient history — and turn it into a structured plan of action. This includes setting realistic goals, prioritizing interventions, and evaluating outcomes. For example, if a patient is at risk for pressure injuries, the care plan might include frequent repositioning, specialized mattresses, and skin assessments.
14. Chest Tube and Drain Management
Managing chest tubes and drains is a skill nurses use in critical moments. Students learn to track drainage, ensure the system is sealed, and watch for warning signs such as sudden spikes in output or patient distress. For example, a sudden increase in bloody drainage could signal internal bleeding. Spotting it early allows the team to act before the situation escalates.
15. Ventilator Care
Ventilator care is a critical competency for nurses working with patients who cannot breathe effectively on their own. Mechanical ventilation supports oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal through an artificial airway — either an endotracheal tube (ETT) or a tracheostomy — and it’s a lifesaving intervention for people with respiratory failure, trauma, or postsurgical complications.
Nursing students learn how to operate these complex machines safely, including reading alarms, interpreting waveforms, and troubleshooting issues like a kinked tube, mucus buildup, or accidental disconnection.
16. Pain Assessment and Management
Pain is one of the main reasons patients come to the hospital, and knowing how to manage it is a key nursing skill. Nursing students learn to read both what patients say and what their bodies show — from facial expressions and body language to changes in vital signs. They also practice a variety of ways to ease pain, from medications to simple alternative techniques like repositioning, heat or cold therapies, and relaxation strategies.
16. Pressure Injury Prevention
Preventing pressure injuries (bedsores) is a critical part of nursing care, especially for patients who are immobile or critically ill. Nursing students learn to assess skin regularly, identify early signs of redness or breakdown, and implement interventions like repositioning schedules, pressure-relieving mattresses, and proper nutrition.
17. CPR, First Aid, and Code Response
Emergencies can happen in an instant, and nurses are always on the front lines. Nursing students are trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for adults, children, and infants, along with basic first aid for choking, bleeding, or fractures. They also learn how to respond during hospital codes — including code blue scenarios for cardiac or respiratory arrest.
Training emphasizes quick, confident action: recognizing emergencies, initiating life-saving interventions,and flawless teamwork — essential basic nursing skills for saving lives when every second counts.
18. Hand Washing
Did you know that handwashing is not just a routine — it’s a technical skill that can prevent the spread of deadly infections in hospitals? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), healthcare workers should scrub all hand surfaces — palms, backs, between fingers, thumbs, and fingertips — for at least 40–60 seconds when using soap and water, or until the alcohol-based sanitizer is completely dry.
By washing hands correctly before and after patient contact, handling equipment, or performing procedures, they dramatically reduce the risk of spreading infections and protect themselves, their colleagues, and their patients.
19. Using Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a cornerstone of infection control and safety in healthcare settings. Nursing students learn to select and use PPE according to the level of precaution required — from standard gloves and masks for routine care, to gowns, eye protection, and respirators for higher-risk situations such as contact, droplet, and airborne.
Training emphasizes proper donning and doffing techniques to prevent contamination, as well as knowing when each level of PPE is necessary.
20. Electronic Health Record Management
You’ve probably heard the phrase, “If it’s not documented, it didn’t happen.” Nursing students learn that accurate charting is more than ticking boxes — it’s also a legal and clinical necessity. Proper documentation ensures that every member of the healthcare team has access to up-to-date information, which improves patient safety and continuity of care.
There are multiple electronic health record (EHR) systems available, and you’ll likely be exposed to several during your clinical rotations. Some of the most popular include Epic, Cerner, and Allscripts.
21. Specialty Skills
Nursing students rotate through a variety of specialty areas during school, each teaching unique skills. For example, during a psychiatric rotation, you’ll learn therapeutic communication techniques, crisis intervention strategies, and substance-specific withdrawal symptoms management. In contrast, in a pediatric rotation, you’ll gain skills in growth and developmental assessments, pediatric medication calculations, and age-specific immunization schedules.
Basic Nursing Skills: FAQ
What are essential hard skills for nursing?
Essential hard skills are the technical abilities nurses must master to provide safe and effective patient care. These include administering medications, inserting IV lines, managing catheters, and using medical equipment like ventilators.
Hard vs. soft skills: What’s the difference?
Hard skills are teachable, measurable, and technical — like catheter insertion, blood pressure measurement, or wound debridement. On the other hand, soft skills include effective communication, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving. Both types of skills are crucial for a well-rounded nursing practice.
Can core nursing skills be applied across all nursing specialties?
Yes. Basic nursing skills training includes essential competencies such as taking vital signs, administering medications, and assisting with patient mobility. These skills form the foundation for nursing practice and are applicable across all nursing specialties — whether in med-surg, geriatric care, or community health. However, each specialty has additional skills that build on these fundamentals.
It’s Time to Find Your Job Match
Whether you’re just developing your basic nursing skills or bringing years of experience to the bedside, IntelyCare helps connect you with quality job opportunities that align with your background and preferences. Sign up today and start exploring jobs made for your level.
