Quality Improvement in Nursing: FAQ and Examples

Healthcare leaders and administrators play a vital role in improving patient outcomes. As a manager of a nursing facility, you’re likely juggling several responsibilities, from allocating resources to supporting the nursing professionals on your staff. You know that you want to prioritize quality improvement in nursing, but are left with questions about how to get started.
The idea of quality healthcare is broad, with large- and small-scale implications. In this article, we’ll explain how this concept is measured, review examples of quality improvement in nursing, and identify key areas of focus when implementing quality improvement initiatives at your facility.
What Is Quality Improvement in Nursing? Facility FAQ
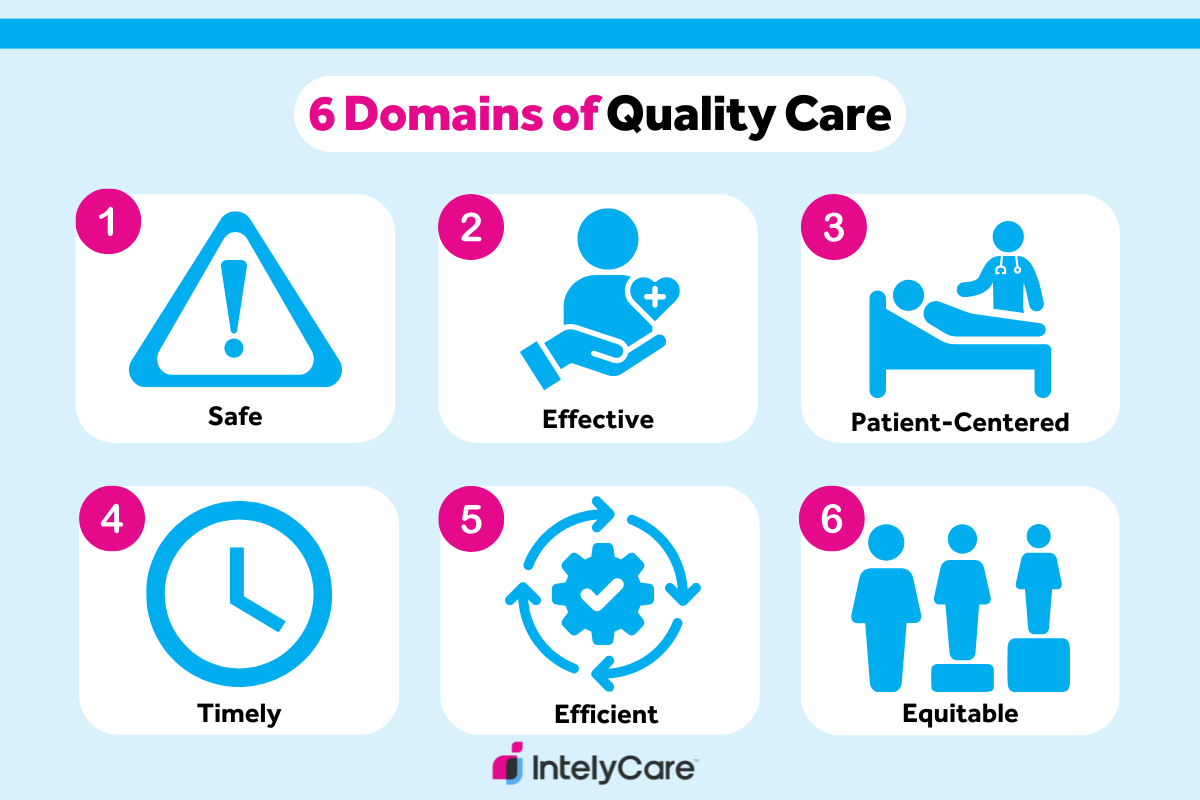
Quality of care in nursing and other health professions measures the degree to which care being delivered follows evidence-based guidelines and helps improve patient outcomes. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) outlines six domains of quality care:
- Safe. Avoid injuring or harming patients with care that is intended to help them by promoting a culture of safety.
- Effective. Offer evidence-based care that achieves desired health outcomes.
- Patient-centered. Provide care that is respectful of individual patient preferences, needs, and values.
- Timely. Deliver care in a prompt manner, reducing wait times and delays in treatment and diagnosis.
- Efficient. Limit the waste of resources, including time, equipment, supplies, energy, and ideas.
- Equitable. Provide consistent care across different populations regardless of gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, location, or other characteristics.
What Are Some Quality of Care in Healthcare Examples?
The best way to understand how these care domains work in practice is to compare examples of both high- and low-quality care. Review the following simplified scenarios:
| Scenario 1 (Patient-Centered Care): A nurse is assigned to give a bed bath to a patient who feels embarrassed about receiving one. | |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Care | The nurse notices the patient’s discomfort and politely asks if she’d prefer to get one at a later time or if there’s anything she can do to make her feel less vulnerable during the procedure. |
| Low-Quality Care | The nurse doesn’t notice the patient’s discomfort and proceeds to give a bed bath as quickly as possible in order to get her tasks done for the day. |
| Scenario 2 (Safety): One nurse on a unit calls out sick for the day, and the patient volume well exceeds the number of nurses available to deliver safe care. | |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Care | The nurse manager calls in a float nurse to help even out the patient load and prevent the other nurses from getting overwhelmed. |
| Low-Quality Care | The nurse manager decides to assign another nurse two extra patients because she knows this particular nurse works quickly. The unexpected workload causes the nurse to make several medical errors throughout her shift. |
What Is the Importance of Quality Improvement in Nursing?
Quality nursing care is a foundational concept of medical practice. Quality care leads to improved patient outcomes — benefits to the health status and quality of life for patients or residents — which is a primary goal of healthcare organizations.
Unfortunately, the U.S. healthcare system often falls behind that of other countries. In fact, U.S. healthcare is among the most expensive in the world, yet studies show that the hefty price tag is often met with care that fails to meet expectations.
Prioritizing high quality in your facility is also important because it’s regulated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and can be tied to funding. CMS assesses quality measures to maintain accountability and address quality of care issues in facilities and residences that receive Medicare or Medicaid.
What Are the Different Quality Improvement Models?
Effective change requires planning and organization, especially when it comes to quality improvement in nursing. Examples of commonly used quality improvement models, and explanations of each, are included in the table below.
|
|
|
|---|---|
| Six Sigma | Processes are designed specifically to minimize variation, limit errors, and reduce waste. |
| Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) | Change is planned, implemented, evaluated for success, and refined based on the success of the initiative. |
| Lean Methodology | Practices are developed to maximize value (for facilities and patients) and minimize operational waste. |
| Total Quality Management (TQM) | Every staff member is encouraged to maintain high work standards through continuous learning. |
What Are Some Common Barriers to Quality Improvement in Nursing?
Before you implement any quality improvement initiatives, you’ll want to understand common barriers that could impede care delivery. Research has shown that different types of barriers can stem from all levels of the healthcare system, including the patient, health professional, and facility. The most common barriers include:
- Poor communication. A lack of communication between any parties in the care process can lead to low-quality care. For instance, a facility leader who doesn’t communicate patient care goals to their nursing team can dampen teamwork, worsening care delivery as a whole.
- Lack of resources. Facilities that lack evidence-based resources are unable to support or train their staff to deliver care that aligns with up-to-date, research driven recommendations. This can lead to poor care practices and impact patient outcomes.
- Staff burnout. Burnout among staff can lead to more nurse turnover. Not only does this create unexpected gaps in staffing, but it also makes it difficult to provide consistent and safe patient care.
How to Improve Quality of Care in Healthcare: 5 Tips
Now that you understand the benefits of quality improvement in healthcare, you’re likely wondering how to take steps to improve the care provided at your facility. Use the ideas below as a starting point when planning new initiatives.
1. Prioritize Training and Education
The nursing staff at your facility or residence is key to improving quality. Continuing education and training are essential to ensuring that your staff is current in their understanding of the latest treatments and procedures. Targeted education and training can also prevent moral injury by helping your nursing staff understand the intricacies of the illnesses their patients commonly experience.
For example, nurses serving a geriatric population can be educated about conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. This not only will equip them to provide safer and more effective care, but the increased vocational confidence could reduce nurse turnover levels in your organization.
Another way to ensure your nursing staff is properly trained and has access to professional development resources is to work with a trusted staffing partner that hires nurses as W2 employees. Not only is there substantial legal and financial risk of misclassification when hiring 1099 contractors and managing them as employees, but they don’t necessarily receive the proper support and training that your facility may require to deliver quality care.
2. Increase Access to Care
If a patient isn’t able to access care in a timely manner, their outcomes will be negatively affected. Reducing barriers to care is imperative to high-quality care, such as ensuring that services are accessible in underserved areas and addressing physical limitations like transportation and cost.
In addition to physical access, make sure that your facility is considering cultural factors that could impact access to care: language, beliefs, and customs. Take steps to overcome communication barriers, connect with community groups, and educate staff members on how differing customs could impact a patient’s healthcare preferences.
3. Engage Patients and Families
Throughout their healthcare experience, patients and their families should be encouraged to ask questions, express concerns, and be included in the care process. Accounting for patient perspectives is integral to shared decision-making. This is an important part of patient-centered care that can lead to improved patient satisfaction and health outcomes, lowered costs, and special recognitions and designations awarded by outside agencies.
4. Improve Communication
Communication is key to quality improvement in nursing. Focus on improving communication between staff and patients or families, ensuring that explanations of diagnoses, treatments, and medications are clear and understandable.
It’s also important to facilitate communication among your staff. Nursing professionals often have innovative solutions to problems, so it’s important that your nurse administrators are open to feedback and encourage innovation. Care quality benefits when all members of the healthcare team work together, collaborating and contributing to continuous improvement.
5. Measure and Monitor Quality
Once you’ve initiated a clinical change, it’s important to track the progress of your quality improvement project . Examples of factors to consider include patient health outcomes and satisfaction scores, clinical processes, medical errors, and utilization of healthcare resources. You can also hire a chief quality officer to oversee this process.
If you need more guidance, the CMS measure inventory provides a repository of evidence-based measures that are used to assess quality of medical care. You can use this repository to narrow down measures that are most relevant to your facility.
Frequent reflection is essential to identifying where improvements can be made and if new initiatives are effective. Make sure you commit to evidence-based practices by using the best available research to guide the healthcare choices in your facility.
6. Set Tangible Goals
Monitoring quality will enable you to target specific areas of care delivery that can inform goal setting. It can be helpful to set tangible and tailored goals for your facility so you can identify when your efforts are coming to fruition. Goal setting can also help you communicate the importance of quality improvement initiatives to your staff and build a sense of teamwork as you work toward these goals together.
If you’re setting goals, it’s important to make them as precise as possible. This can be done by using quantitative measures that focus on the six different domains that make up quality of care. In this way, you can make realistic yet productive strides toward providing safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care.
7. Relay Progress Back to Staff
As you strive toward improving how you deliver care at your facility, it’s important to keep your staff engaged throughout every step of the process. In addition to soliciting ideas on how to elevate care, you should also make efforts to report any progress back to your staff to keep them engaged.
This allows you to show appreciation for staff who contribute efforts that elevate patient care and celebrate the hard work that your team has put in as a whole. Acknowledging progress can also help your staff feel seen and heard, which is one of many ways to help cultivate a healthy work environment and reduce staff turnover.
Want to Find More Ways to Improve Care Quality?
Quality improvement in nursing requires healthcare leaders to make a commitment to continuous learning. At Intelycare, our team of clinical and legal experts has developed hundreds of useful resources and insights to keep you in the know.